1. Let
A = { a , b , c ,d , e } and B={ a , b , c , d , e , f , g , h }then A - B is
1) A
2) B
3) A
Ç
B
4) F
2. A
Relation R on a Set A is called a partial order, if (A, R) is
1) Reflexive relation
2) Symmetric relation
3) Reflexive, Anti-Symmetric and Transitive relation
4) Reflexive, Symmetric and Transitive relation
1) Reflexive relation
2) Symmetric relation
3) Reflexive, Anti-Symmetric and Transitive relation
4) Reflexive, Symmetric and Transitive relation
3. If
A and B are two independent events such that P(A) =0.5 and P)
(
A È
B =
0.8 then
P(B) is
1) 0.6
2) 0.5
3) 0.8
4) 0.05
P(B) is
1) 0.6
2) 0.5
3) 0.8
4) 0.05
4. A
Context – free grammar G is ambiguous if there is some string w belongs to L(G)
that has two distinct
1) Graph only
2) Parse trees
3) Grammars
4) Ordered
that has two distinct
1) Graph only
2) Parse trees
3) Grammars
4) Ordered
5. An
FSM can be considered to be a TM
1) Of finite tape length, rewinding capability and unidirectional tape movement
2) Of finite tape length, without rewinding capability and unidirectional tape
movement
3) Of finite tape length, without rewinding capability and bidirectional tape
movement
4) Of finite tape length, rewinding capability and bidirectional tape movement
1) Of finite tape length, rewinding capability and unidirectional tape movement
2) Of finite tape length, without rewinding capability and unidirectional tape
movement
3) Of finite tape length, without rewinding capability and bidirectional tape
movement
4) Of finite tape length, rewinding capability and bidirectional tape movement
6. The
functional difference between SR flip-flop and JK flip-flop is that
1) JK flip-flop is faster than SR flip-flop
2) JK flip-flop has a feedback path
3) JK flip-flop accepts both inputs
4) JK flip-flop does not require external clock
1) JK flip-flop is faster than SR flip-flop
2) JK flip-flop has a feedback path
3) JK flip-flop accepts both inputs
4) JK flip-flop does not require external clock
7. The
black box in the following figure consists of a minimum complexity circuit that
uses only AND, OR and NOT gates. The function f(x, y, z) = 1 whenever x, y are
different and 0 otherwise. In addition the 3 inputs x, y, z are never all the same value.
Which of the following equation lead to the correct design for the minimum
complexity circuit?
uses only AND, OR and NOT gates. The function f(x, y, z) = 1 whenever x, y are
different and 0 otherwise. In addition the 3 inputs x, y, z are never all the same value.
Which of the following equation lead to the correct design for the minimum
complexity circuit?
1) x¢y + xy¢
2) x + y¢z
3) x¢y¢z+ ¢ x y¢ z
4) xy + y¢z + z¢
8. The
dual of the switching function x + yz is:
1) x + yz
2) x + y r z
3) x) ( y + z
4) x) ( y + z
1) x + yz
2) x + y r z
3) x) ( y + z
4) x) ( y + z
9. The
sum of two hexadecimal numbers 23D and 9AA gives the hexadecimal number
1) AF7
2) BF6
3) BE7
4) BE5
1) AF7
2) BF6
3) BE7
4) BE5
10. An
AND gate has 7 input. How many input words are in its truth table?
1) 64
2) 32
3) 16
4) 128
1) 64
2) 32
3) 16
4) 128
11. Functions
defined with class name are called as
1) Inline function
2) Friend function
3) Constructor
4) Static function
1) Inline function
2) Friend function
3) Constructor
4) Static function
12. Identify
the incorrect file opening mode from the following.
1) r
2) w
3) x
4) a
1) r
2) w
3) x
4) a
13. Choose
the correct statement that is a combination of these two statements,
Statement 1: char *p;
Statement 2: p = (char*) malloc(100);
1) char p = *malloc(100);
2) char *p = (char*)malloc(100);
3) char *p = (char) malloc(100);
4) None of the above
Statement 1: char *p;
Statement 2: p = (char*) malloc(100);
1) char p = *malloc(100);
2) char *p = (char*)malloc(100);
3) char *p = (char) malloc(100);
4) None of the above
14. Which
operator is having the highest precedence?
1) postfix
2) unary
3) shift
4) equality
1) postfix
2) unary
3) shift
4) equality
15. The
operator used for dereferencing or indirection is
1) *
2) &
3) ->
4) ->>
1) *
2) &
3) ->
4) ->>
16. A
relation is in ––––––––––– if an attribute of a composite key is dependent on
an
attribute of other composite key.
1) Normal Form
2) BCNF
3) 1NF
4) 2NF
attribute of other composite key.
1) Normal Form
2) BCNF
3) 1NF
4) 2NF
17. –––––––––––
refers to the accuracy and consistency of data stored in a database.
1) Entity
2) Attributes
3) Primary Key
4) Data Integrity
1) Entity
2) Attributes
3) Primary Key
4) Data Integrity
18. –––––––––––
act as a cross-reference between tables.
1) Primary Key
2) Candidate Key
3) Foreign Key
4) Super Key
1) Primary Key
2) Candidate Key
3) Foreign Key
4) Super Key
19. A
synonym is an alias for ––––––––––– object
1) Schema
2) Sequence
3) Segment
4) View
1) Schema
2) Sequence
3) Segment
4) View
20. –––––––––––
type of relational database which incorporate concepts of object
database
1) Functional object system
2) Behavioral relational system
3) Extended relational system
4) Extended objects system
database
1) Functional object system
2) Behavioral relational system
3) Extended relational system
4) Extended objects system
21. The
Postfix equivalent of prefix expression /+PQ-RS is
1) PQ+RS/-
2) PQ+RS-/
3) PQRS+-/
4) PQ+/RS-
1) PQ+RS/-
2) PQ+RS-/
3) PQRS+-/
4) PQ+/RS-
22. Which
of the following data structure is most suitable for implementing recursive
computations?
1) Stack
2) Queue
3) Array
4) Linked List
computations?
1) Stack
2) Queue
3) Array
4) Linked List
23. Which
type of traversal on a binary tree resembles the depth first search of a graph?
1) Postorder
2) Preorder
3) Inorder
4) Level Order
1) Postorder
2) Preorder
3) Inorder
4) Level Order
24. Find
the indegree of node V2 for a directed Graph G, represented in
the following
adjacency matrix
1) 0
2) 1
3) 2
4) 3
adjacency matrix
1) 0
2) 1
3) 2
4) 3
25. The
average search time of hashing with linear probing will be less if the load
factor
1) is far less than one
2) equals one
3) is far greater than one
4) is greater than one
1) is far less than one
2) equals one
3) is far greater than one
4) is greater than one
26. Which
of the following connects two or more networks and provides necessary
translation?
1) Protocol
2) Interface
3) Gateway
4) Physical medium
translation?
1) Protocol
2) Interface
3) Gateway
4) Physical medium
27. "BAUD"
rate means
1) The number of bits transmitted per unit time
2) The number of bytes transmitted per unit time
3) The rate at which the signal changes
4) The number of bits transmitted per unit second
1) The number of bits transmitted per unit time
2) The number of bytes transmitted per unit time
3) The rate at which the signal changes
4) The number of bits transmitted per unit second
28. The
entire hostname has a maximum of
1) 255 characters
2) 127 characters
3) 63 characters
4) 31 characters
1) 255 characters
2) 127 characters
3) 63 characters
4) 31 characters
29. Which
of the following devices direct network traffic based not by MAC addresses but
by software-configured network addresses?
1) Router
2) Hub
3) Bridge
4) NIC
by software-configured network addresses?
1) Router
2) Hub
3) Bridge
4) NIC
30. Telephone
companies normally provide a voltage of ––––––––––– to power telephones
1) +24 volts DC
2) –24 volts DC
3) +48 volts DC
4) –48 volts DC
1) +24 volts DC
2) –24 volts DC
3) +48 volts DC
4) –48 volts DC
31. The
identification of common sub-expression and replacement of run-time
computations by compile-time computations is
1) local optimization
2) loop optimization
3) constant folding
4) data flow analysis
computations by compile-time computations is
1) local optimization
2) loop optimization
3) constant folding
4) data flow analysis
32. –––––––––––
is the first step in the evolution of programming languages.
1) machine language
2) assembly language
3) code language
4) high level language
1) machine language
2) assembly language
3) code language
4) high level language
33. Which
of the following allows data transfer between memory and peripherals?
1) Microprocessor
2) DMA technique
3) Register
4) Decoder
1) Microprocessor
2) DMA technique
3) Register
4) Decoder
34. What
is the function of YACC command in compilation process?
1) token splitting
2) parser generation
3) intermediate-code generation
4) code generation
1) token splitting
2) parser generation
3) intermediate-code generation
4) code generation
35. From
this context-free grammar E => E * E,
which of the following can be arrived by leftmost-derivation?
(a) E => E * I
(b) E => I * E
(c) E => a * E
1) only (a)
2) only (b)
3) only (c)
4) both (b) and (c)
which of the following can be arrived by leftmost-derivation?
(a) E => E * I
(b) E => I * E
(c) E => a * E
1) only (a)
2) only (b)
3) only (c)
4) both (b) and (c)
36. Fork
is
1) the dispatching of a task
2) the creation of a new job
3) the creation of a new process
4) increasing the priority of a task
1) the dispatching of a task
2) the creation of a new job
3) the creation of a new process
4) increasing the priority of a task
37. If
there are 32 segments, each of size 1 K byte, then the logical address should
have
1) 13 bits
2) 14 bits
3) 15 bits
4) 16 bits
1) 13 bits
2) 14 bits
3) 15 bits
4) 16 bits
38. Which
of the following scheduling algorithms is non-preemptive?
1) Round Robin
2) First-In First-Out
3) Multilevel Queue Scheduling
4) Multilevel Queue Scheduling with Feedback
1) Round Robin
2) First-In First-Out
3) Multilevel Queue Scheduling
4) Multilevel Queue Scheduling with Feedback
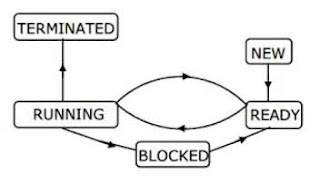
39. The
process state transition diagram in the following Figure is representative of
1) a batch operating system
2) an operating system with a preemptive scheduler
3) an operating system with a non-preemptive scheduler
4) a uni-programmed operating system
40. The
differences between malloc( ) and calloc( ) are:
1) Malloc is used for dynamic allocation of memory, while calloc can't be used for
that purpose
2) Malloc needs only one argument. while calloc needs two.
3) unlike malloc, calloc allocates memory and initializes it to 0.
4) Both (2) and (3)
1) Malloc is used for dynamic allocation of memory, while calloc can't be used for
that purpose
2) Malloc needs only one argument. while calloc needs two.
3) unlike malloc, calloc allocates memory and initializes it to 0.
4) Both (2) and (3)
41. The
correct formula for Schedule performance index is,
1) SPI = BCWS/BCWP
2) SPI = BCWP/BCWS
3) SPI=BCWP – BCWS
4) SPI=BCWP + BCWS
1) SPI = BCWS/BCWP
2) SPI = BCWP/BCWS
3) SPI=BCWP – BCWS
4) SPI=BCWP + BCWS
42. SRD
stands for
1) Software Requirements Definition
2) Structured Requirements Definition
3) Software Requirements Diagram
4) Structured Requirements Diagram
1) Software Requirements Definition
2) Structured Requirements Definition
3) Software Requirements Diagram
4) Structured Requirements Diagram
43. Changes
made to an information system to add the desired but not necessarily the
required features is called
1) Preventative maintenance
2) Adaptive maintenance
3) Corrective maintenance
4) Perfective maintenance
required features is called
1) Preventative maintenance
2) Adaptive maintenance
3) Corrective maintenance
4) Perfective maintenance
44. Optimization,
Defect Prevention, and Quality Control. Its come under the
1) CMM Level 2
2) CMM Level 3
3) CMM Level 4
4) CMM Level 5
1) CMM Level 2
2) CMM Level 3
3) CMM Level 4
4) CMM Level 5
45. What
would be investigated during Requirements analysis?
1) System performance, Test Scheduling, Organizational Structure
2) Languages, Platforms, Competition
3) System Context, User Populations, User Tasks
4) Verification, Formal Methods, Accuracy
1) System performance, Test Scheduling, Organizational Structure
2) Languages, Platforms, Competition
3) System Context, User Populations, User Tasks
4) Verification, Formal Methods, Accuracy
46. –––––––––––
command lists the host name, PVM daemon task id, architecture type,
and relative speed rating.
1) conf
2) ps-a
3) setenv
4) id
and relative speed rating.
1) conf
2) ps-a
3) setenv
4) id
47. DHCP
stands for
1) Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
2) Digital Host Communication Provider
3) Digital Host Communication Protocol
4) Dynamic Host Configuration Provider
1) Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
2) Digital Host Communication Provider
3) Digital Host Communication Protocol
4) Dynamic Host Configuration Provider
48. Which
IEEE 802.11 Extension provides AES and DES security standards?
1) 802.11a
2) 802.11b
3) 802.11g
4) 802.11i
1) 802.11a
2) 802.11b
3) 802.11g
4) 802.11i
49. Given
desired class C and population P, lift is defined as
1) the probability of class C given population P divided by the probability of C
given a sample taken from the population.
2) the probability of population P given a sample taken from P.
3) the probability of class C given a sample taken from population P.
4) the probability of class C given a sample taken from population P divided by the
probability of C within the entire population P.
1) the probability of class C given population P divided by the probability of C
given a sample taken from the population.
2) the probability of population P given a sample taken from P.
3) the probability of class C given a sample taken from population P.
4) the probability of class C given a sample taken from population P divided by the
probability of C within the entire population P.
50. A
variation of the star schema that allows more than one central fact table.
1) snowflake schema
2) linked strar schema
3) distributed star schema
4) constellation schema
1) snowflake schema
2) linked strar schema
3) distributed star schema
4) constellation schema
Answer Key
1. 4 26.
3
2. 3 27. 3
3. 1 28. 1
4. 2 29. 1
5. 2 30. 3
6. 3 31. 3
7. 1 32. 2
8. 3 33. 2
9. 3 34. 2
10. 4 35. 4
11. 3 36. 3
12. 3 37. 3
13. 2 38. 2
14. 1 39. 2
15. 1 40. 4
16. 1 41. 3
17. 4 42. 2
18. 3 43. 4
19. 1 44. 4
20. 3 45. 3
21. 2 46. 1
22. 1 47. 1
23. 3 48. 4
24. 4 49. 4
25. 1 50. 4
2. 3 27. 3
3. 1 28. 1
4. 2 29. 1
5. 2 30. 3
6. 3 31. 3
7. 1 32. 2
8. 3 33. 2
9. 3 34. 2
10. 4 35. 4
11. 3 36. 3
12. 3 37. 3
13. 2 38. 2
14. 1 39. 2
15. 1 40. 4
16. 1 41. 3
17. 4 42. 2
18. 3 43. 4
19. 1 44. 4
20. 3 45. 3
21. 2 46. 1
22. 1 47. 1
23. 3 48. 4
24. 4 49. 4
25. 1 50. 4



No comments:
Post a Comment